The Necessity of a China Factory Check
Importing goods from overseas presents significant opportunities for growth and cost reduction. However, it also introduces substantial risk, particularly regarding quality and reliability. Conducting a thorough China factory check is the most critical step for any first-time importer. This preemptive action minimizes fraud, ensures compliance, and verifies production capability.
A successful China factory check moves beyond superficial visits. It involves deep dives into a supplier’s operational, financial, and ethical standing. Furthermore, a professional procurement agent or third-party auditor often executes this complex process. This meticulous vetting is the foundation for a secure and profitable international trade relationship.

Defining the Factory Check Process
The factory check is a systematic audit of a potential supplier’s premises and operations. It serves as an essential due diligence step before placing any significant order. This process confirms that the supplier is who they claim to be and can meet the buyer’s quality and volume requirements.
Key Objectives of the China Factory Check
The primary goal of the factory check is risk mitigation. It confirms the factory is legitimate and not a trading company posing as a manufacturer. Furthermore, it assesses the factory’s capacity, ensuring they can handle the order size and maintain production deadlines.
Additionally, the check verifies quality management systems and adherence to safety standards. For instance, auditors review equipment maintenance records and worker training logs. This thorough inspection confirms whether the factory can consistently produce goods that meet the buyer’s specifications.
Essential Components of the Audit
A comprehensive factory audit covers several critical areas. First, it reviews legal and business documentation, including licenses and certifications. Second, it assesses the factory layout, workflow efficiency, and available machinery. Third, the audit examines the supplier’s quality control (QC) procedures, from incoming raw materials to final packaging.
Moreover, the check investigates social and environmental compliance. This includes looking for evidence of child labor or unsafe working conditions. Ultimately, the factory check provides a complete, objective view of the supplier’s true capabilities.
Role of the Procurement Agent in Factory Checks
For first-time importers, navigating the supplier vetting process in a foreign country can be overwhelming. A professional procurement agent provides invaluable assistance, acting as the buyer’s local representative on the ground.
Agent Responsibilities in the China Factory Check
A skilled China procurement agent is indispensable for executing a successful factory check. They manage all scheduling and communication with the supplier, overcoming language barriers. Furthermore, they possess local knowledge that helps identify subtle red flags that foreign buyers might miss.
The agent often physically conducts the initial site visit or arranges for an independent audit team. They meticulously review all documentation, verifying its authenticity against local databases. Consequently, they provide the buyer with a concise, unbiased report, saving significant time and expense.
Strategic Value of the Agent’s Expertise
The procurement agent brings specialized knowledge to the vetting process. They understand typical local pricing structures and common manufacturing pitfalls in the region. For example, they can recognize when a factory’s stated capacity seems unrealistic.
This expertise ensures the buyer receives accurate information, not just what the supplier wants them to see. Furthermore, the agent acts as an effective intermediary, ensuring audit findings are communicated clearly and necessary corrective actions are implemented by the factory.
The China Factory Check Checklist: Core Sections
To ensure no critical area is overlooked, the China factory check must be structured around specific operational and compliance categories. Each section provides a piece of the puzzle regarding the supplier’s overall reliability.
Section one: Business and Legal Documentation
Verify the factory’s business license, checking the validity and the scope of business. Ensure the legal name on the license matches all correspondence. Furthermore, review export permits and any necessary product certifications, such as ISO nine thousand one or CE marks.
Confirm ownership structure and registration capital to assess financial stability. Additionally, check the date of establishment to gauge experience. This thorough legal review is crucial for confirming legitimacy and minimizing fraud risk.
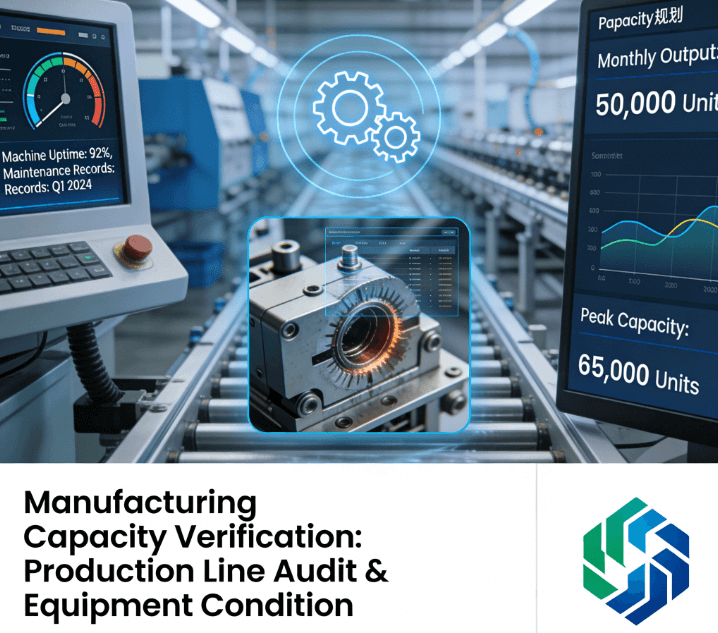
Section two: Production Capacity and Facilities
Evaluate the size of the manufacturing facility and the condition of the machinery. Assess the factory’s total daily or monthly output capacity for the specific product being sourced. Furthermore, verify that key equipment is owned, not leased, which indicates a greater investment.
Observe the general cleanliness, organization, and maintenance procedures. For instance, auditors check for clearly labeled material storage and adequate lighting. This inspection ensures the factory can scale production while maintaining quality standards.
Section three: Quality Control (QC) Systems
The QC section is arguably the most vital part of the China factory check. Review the quality manual and the organizational structure of the QC department. Verify incoming material inspection procedures and in-process checks on the assembly line.
Furthermore, examine records of final product testing and outgoing quality assurance. For example, auditors check how non-conforming products are isolated and handled. Strong, documented QC procedures are the clearest indicator of a reliable long-term supplier.
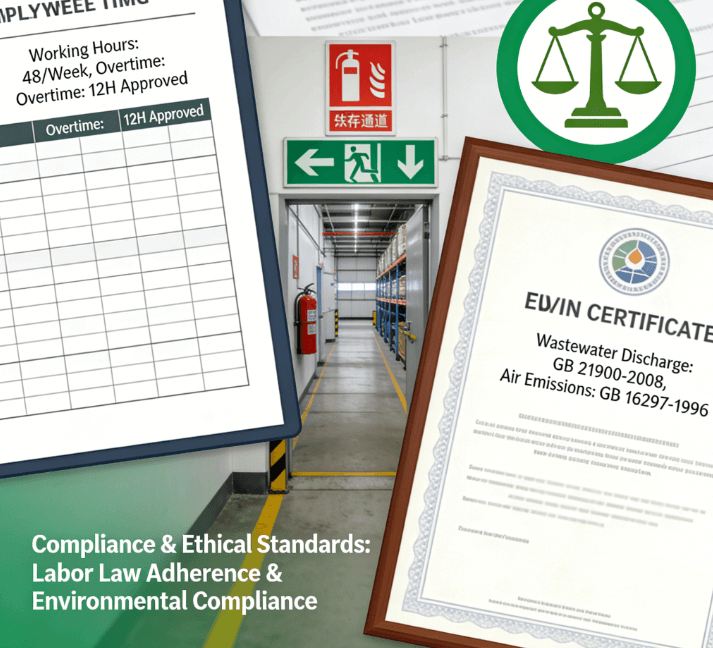
Section four: Social and Environmental Compliance
Ensure the factory meets basic ethical standards. Review labor records to confirm legal working hours and ages. Furthermore, inspect safety measures, including fire exits, ventilation, and protective gear provided to workers.
Check for environmental permits and waste disposal procedures. For instance, auditors look for proper chemical storage and disposal of wastewater. This compliance review protects the buyer from association with unethical labor practices and regulatory violations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Factory Check
Even with a comprehensive checklist, first-time importers often make preventable errors. Avoiding these common pitfalls ensures the factory check yields accurate and actionable information.
Relying Solely on Supplier-Provided Information
Never accept documentation or photographs from the supplier at face value. Suppliers often use highly edited pictures or generic certifications. Always insist on an independent, physical China factory check executed by a neutral third party.
Furthermore, use public databases to cross-reference legal registration numbers. This skepticism is not distrust; it is simply smart business practice in international trade.
Skipping the Initial Visit
Some importers skip the visit, relying on certifications alone to save costs. However, certifications confirm systems are in place, not that they are followed daily. A physical visit reveals the factory’s true operational reality, including staff morale and housekeeping.
The cost of a faulty batch of goods far outweighs the expense of the initial factory check. This visit provides critical visual confirmation of the supplier’s capabilities.
Lack of Clear Audit Specifications
Before any visit, provide the auditor or agent with precise, product-specific inspection points. Generic checklists may miss crucial details relevant to the imported product. For instance, if importing electronics, emphasize testing equipment calibration.
Clarity ensures the audit team focuses on the buyer’s unique needs. This tailored approach maximizes the value of the China factory check report.
Strategic Value of the China Factory Check
The factory check provides value far beyond simple compliance; it is a strategic investment in supply chain stability. It establishes a strong foundation for a long-term, mutually beneficial relationship with the supplier.
This due diligence allows the importer to negotiate from a position of strength and knowledge. Furthermore, by identifying reliable partners early, companies can focus their resources on market development rather than firefighting supply problems. The rigorous China factory check is a competitive advantage.
Practical Example: The Apparel Importer’s Success
A US startup planned to import a new line of sportswear. They initially found a seemingly perfect supplier online. Before placing the full order, they hired a procurement agent to conduct a China factory check.
The agent’s audit revealed that the factory outsourced seventy percent of its stitching work to a smaller, unregulated subcontractor. Furthermore, the main factory’s QC system was deficient. Armed with this knowledge, the importer avoided a costly batch of non-compliant goods. They used the agent’s network to find a fully compliant, verified factory, ensuring a successful and ethical product launch.
Future Trends in Global Supplier Vetting
The future of factory checking is evolving rapidly, driven by technology and increasing demands for ethical sourcing. Digital tools will soon enhance the work of the human auditor.
Integration of AI and Remote Auditing
Future factory checks will increasingly integrate AI and remote sensing technology. For example, drone footage could verify facility size, and IoT sensors could monitor production output in real-time. This technology assists the human auditor by providing continuous, objective data.
Furthermore, blockchain technology could be used to store immutable compliance records. This creates a secure, verifiable history of a factory’s performance and ethical standards.
Emphasis on Ethical and Environmental Audits
The focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards will intensify. Future factory checks will place greater weight on quantifiable environmental impact and detailed labor practices. Suppliers will need to prove not only product quality but also their commitment to sustainability.
This trend ensures that sourcing decisions align with corporate social responsibility mandates. The China factory check will become a vital tool for ethical supply chain management.
Conclusion: Securing Your Supply Chain
The comprehensive China factory check is the most essential tool for any importer seeking to secure a stable and reliable supply chain. It mitigates risks, verifies quality, and ensures ethical sourcing practices. By utilizing a structured checklist and leveraging the expertise of a procurement agent, companies can confidently establish profitable relationships in international trade. This due diligence is the key to successful global importing.



